Welcome back to our informative, ENT blog. Today, we are sharing more on the ever so important eardrum and eustachian tube. The eardrum is a vital part to the ear anatomy, and we are going to share what experienced ENT doctors can do for treatment and healing.
The eardrum:
An eardrum is no insignificant part of the body. Without it, we would not be able to hear the same we do now with a normally functioning eardrum. The eardrum may become injured or infected for a number of reasons.
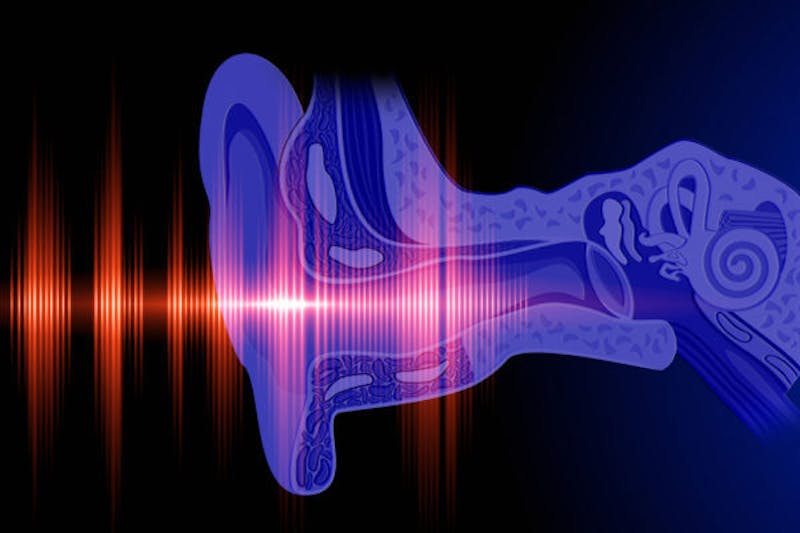
First off, we should discuss the role of the eardrum to better understand its importance. The ear consists of three major areas. We have an inner ear, middle ear, and outer inner. Both the eardrum and three small bones located in the middle ear amplify the vibrations.
The amplification happens as it passes through the inner ear. From there, the vibrations pass through fluid in a snail-shaped, or shell-shaped, structure in the inner ear. This radically shaped structure is called the cochlea.
There are thousands of tiny hairs attached to the nerve cells in the cochlea. Those tiny hairs help translate sound vibrations into electrical signals. The electrical signals are then transmitted to the brain. The brain is what magically turns these signals into sounds.
The function of a eustachian tube:
There is one eustachian tube in each ear. The eustachian tubes are a pair of narrow tubes. They run from each middle ear to high in the back of the throat. This is all behind the nasal passages.
The nasopharynx is the part of the throat which consists of the upper throat and back of the nasal cavity. The eustachian tubes are closed most of the time. They open only when necessary.
The end of a eustachian tube, closest to the throat, opens and closes for multiple reasons. They open and close to regulate the air pressure in the middle ear, to refresh air in the ear, and to drain normal secretions from the middle ear.
A eustachian tube will open and close when yawning, chewing, swallowing, and to allow air to travel through the middle ear to the nasopharynx. You may have experienced the need to open your mouth wide, swallow, or yawn when atmospheric pressure changes rapidly. This happens during air travel and scuba diving.
Pain in malfunction:
When the eustachian tube does not open enough to equalize the pressure, it can cause a few uncomfortable symptoms. Ringing in the ear, dizziness, and discomfort are just a few symptoms that may come along after the eustachian tube does not open enough.
Come back next time for the next segment of our ear anatomy series. We hope to hear from you soon to schedule a regular exam or to check on any ear pain. Our ENT specialists offer hearing testing as well.
Staff Writer

